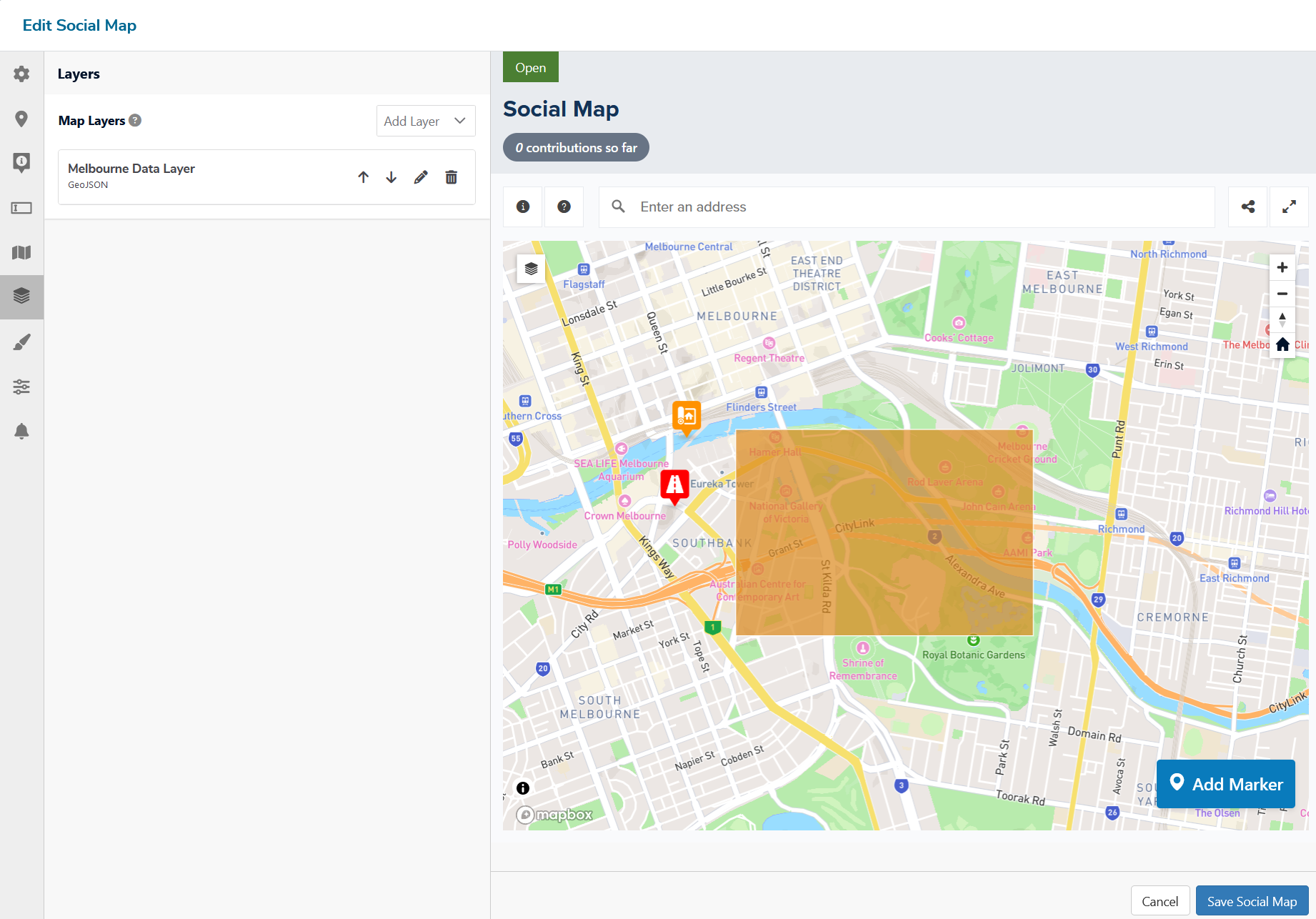
Spatial data layers can be added to the base map to provide further
information and context to the visitor. Points, lines and polygons can
all be added to the Social Map. This can be useful to highlight areas or
features related to the activity.
The Social Map uses the WGS 1984 geographic coordinate system. When
uploading your spatial data layers, your files will automatically be
converted into this system.
Map layers can be added from .shp or .geojson files. To add layers via GeoJSON or Shapefile:
- Navigate to the 'Layers’ tab and and select 'Add Layer’.
- Choose either ‘GeoJSON’ or ‘Shapefile’ from the dropdown.
- Name your layer and upload the file.
- Select the blue ‘Save’ button to save your layer.
- Select the blue ‘Save Social Map' to apply it on the Social Map.
When
working with the shapefile format, it is important to note that these
are comprised of multiple files, that necessarily include .shp, .shx and
.dbf, but can also include a variety of optional files with different
formats.
To use shapefiles within Social Pinpoint, all relevant files must be converted to a .zip file in order to be used within the mapping tools.
💡User Tip
If you want to draw your own data layers, but don’t have GIS skills or software, you can use this free tool.
It helps let you easily draw point layers, lines or polygons. Simply
sketch the features, save as .geojson and upload into Social Pinpoint.
Custom data layers can be added to the base
map to provide further information and context to the visitor. Points,
lines and polygons can all be added to the Social Map. To add custom
layers:
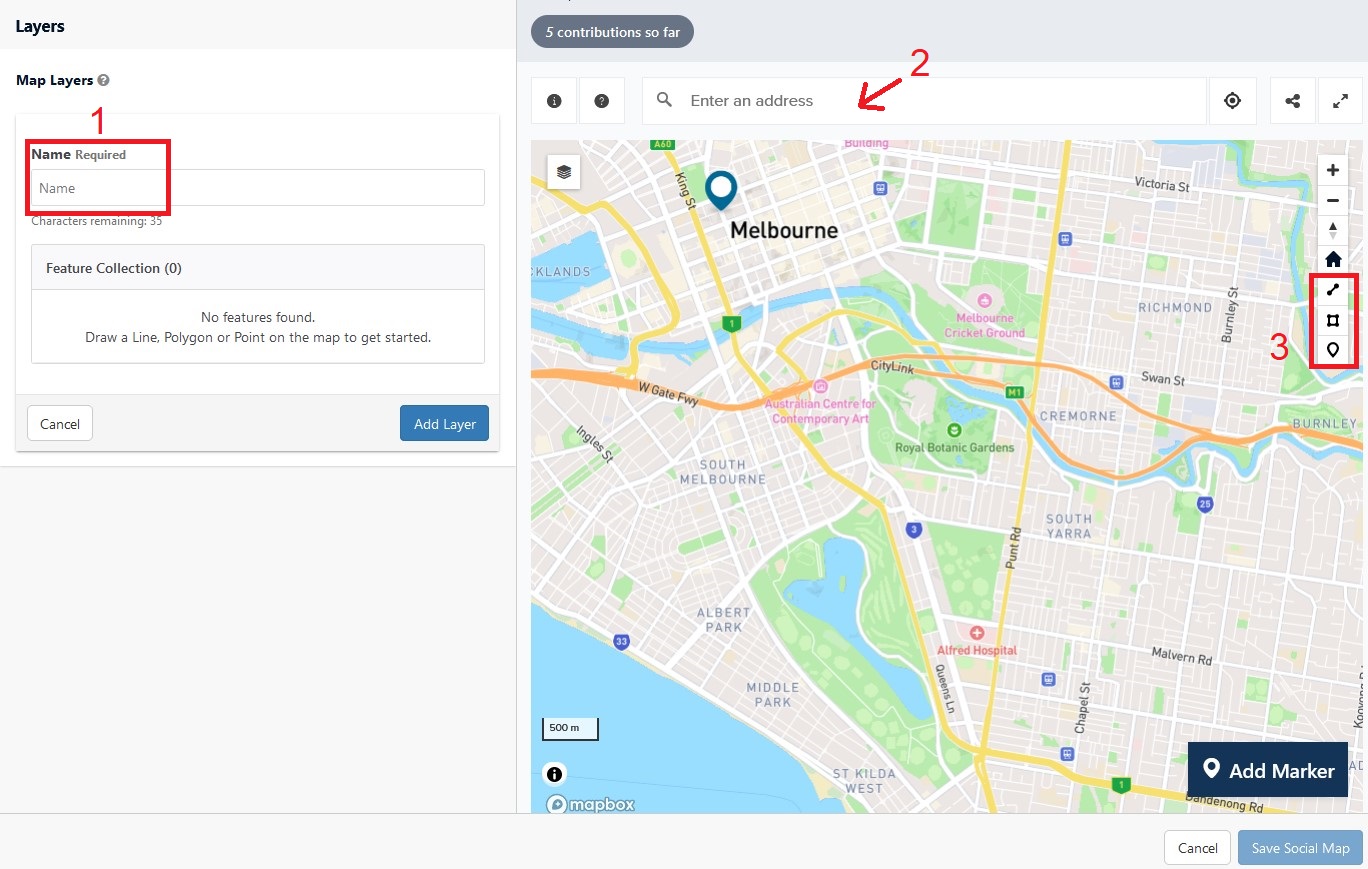
- Give your layer a name in the provided field.
- You
will be presented with a map, which you can enter an address into to
refocus to your desired location. You can use the scroll and zoom
functions provided to see more detail.
- There are three shapes on the right hand side of the map:
- Linestring allows you to draw lines on your map or create shapes using lines.
- Polygon allows you to create polygon shapes on your map
- Marker allows you to drop a pin at a particular point of interest. - Once
you have defined your layer you can create a pop-up with information
and/or an image. Under Feature Collection, select Edit Feature Info and
fill out the relevant information.
- Once you have defined your
layer, you will be able to adjust the stroke colour, width and opacity,
as well as fill colour, fill opacity and dash array.
- When you are finished, select Save Layer.
Images of plans, diagrams or other non-spatial data can be
superimposed on the basemap to give it a spatial context and collect
spatially accurate feedback.
To add a geo-referenced image to the Social Map:
- Navigate to the ‘Layers’ tab, select 'Add Layer' and scroll down to ‘Image’.
- Name your layer and upload your image (jpeg, png or gif).
- Enter
the 'Image Bounds' which are the latitude and longitude coordinates of
the image to position the corners correctly over the map.
*Our Social Map uses the WGS 1984 geographic coordinate system.
- Select the blue ‘Save Layer’ button to save your layer.
Placing an image on the social map you'll need 'two points':
1. Top left point's longitude and latitude.
2. Bottom right point's longitude and latitude.
Please note that images should be North-Facing otherwise it wouldn't display properly.

The coordinates N and W refer to the Latitude and Longitude of point 1. The S and E refer to the Latitude and Longitude of point 2.
Example:

How would I get these coordinates?
There are a couple of tools you can use the most common mapping system would be Google Maps.

Selecting
a point in the map would show the coordinates for that specific point
in a small pop-up window (see image above), once you have the proper
coordinates for the top point you can repeat to get the bottom point
coordinates.
If you want a more accurate box placement, you can enable the '
Define all corners' tick box and it will ask for all four corner's coordinates.










